---
상대위상 존재론: 관계적 위치를 통한 존재의 발현에 대한 프랙탈적 모델
저자: 이라하 무안테
소속: 이론 메타구조 독립연구소
작성일: 2025년 3월 26일
---
초록 (Abstract)
본 논문은 ‘상대위상 존재론’이라는 새로운 철학적 이론을 제안한다. 이 이론은 모든 존재는 고유한 본질이나 절대적 좌표에 의해 정의되는 것이 아니라, 상호작용하는 존재들과의 관계적 위치, 즉 상대적인 위상(Phase)을 통해 나타난다고 주장한다. 천체의 운동과 조류의 군집행동 같은 다양한 스케일의 현상들을 분석함으로써, 이론은 서로 다른 작동 원리를 지닌 시스템들이 유사한 위상적 패턴을 보이며, 결과적으로 프랙탈 구조를 형성한다는 점을 드러낸다. 본 연구는 이러한 존재의 위상적 정의를 수학적으로 일반화하며, 물리학, 생물학, 인지과학 등 다양한 분야에 적용 가능함을 보여준다.
---
1. 서론
“존재란 무엇인가?”라는 질문은 오랫동안 철학, 물리학, 생물학 등 여러 분야에서 제기되어 온 근본적 사유이다. 고전적 존재론은 보통 존재를 고정된 실체나 본질로 간주해왔다. 그러나 상대성이론, 양자역학, 복잡계 이론의 발달과 함께, 존재는 독립적인 실체가 아닌 관계적 구조 속에서만 의미를 갖는 현상으로 재해석되고 있다.
본 논문은 그러한 흐름 속에서 ‘상대위상 존재론(Relational Phase Ontology)’을 제안한다. 이 이론은 모든 존재는 자신 외의 타 존재들과의 위상 차이에 의해 정의된다는 전제를 바탕으로 하며, 이러한 구조가 다양한 스케일에서 **프랙탈적 자기유사성(Self-Similarity)**을 보인다는 사실에 주목한다.
---
2. 이론적 배경
2.1. 천체의 상대 운동
천문학과 상대성이론에 따르면, 우주의 모든 천체는 절대적 중심 없이 다른 질량체에 대한 중력적 관계를 통해 운동한다. 지구는 태양을 공전하고, 태양은 은하 중심을 공전하며, 은하는 우주적 팽창 흐름에 따라 이동한다. 이 모든 운동은 절대 좌표가 아닌 상대 위치의 변화를 통해서만 의미를 갖는다.
2.2. 생물의 집단 행동
까마귀, 잉어, 멸치 떼와 같은 생물 군집의 집단 이동은 중앙 통제자 없이 개체 간 상호작용으로 이루어진다. 특히 조류의 군무는 각 개체가 주변 개체와의 거리, 속도, 방향을 실시간으로 조절함으로써 집단 전체가 유기적 형태를 이루게 된다. 이는 국소적인 위상 정보가 집단 수준의 패턴으로 확장되는 구조다.
---
3. 중심 명제: 위상 차에 의한 존재
본 이론의 핵심 명제는 다음과 같다:
> 존재는 고정된 실체가 아니라, 위상 차이로 정의되는 상호작용의 함수이다.
이를 수학적으로 다음과 같이 표현할 수 있다:
E = f(\Delta \phi_{1}, \Delta \phi_{2}, ..., \Delta \phi_{n})
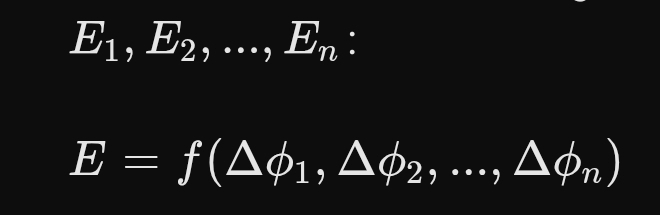
여기서 는 하나의 존재, 은 다른 존재들과의 위상 차이를 의미한다.
이 함수는 존재가 독립적 실체가 아닌, 상대적인 위상 차이 속에서만 감지되고 정의되는 패턴임을 보여준다.
---
4. 스케일 간의 프랙탈 유사성
우주적 스케일부터 생물학적, 사회적 스케일까지 다양한 영역에서 관찰되는 구조는 프랙탈적 자기유사성을 보인다. 즉, 작동 원리는 다르지만 위상 차를 기반으로 한 관계망 구조는 스케일을 초월해 반복된다.
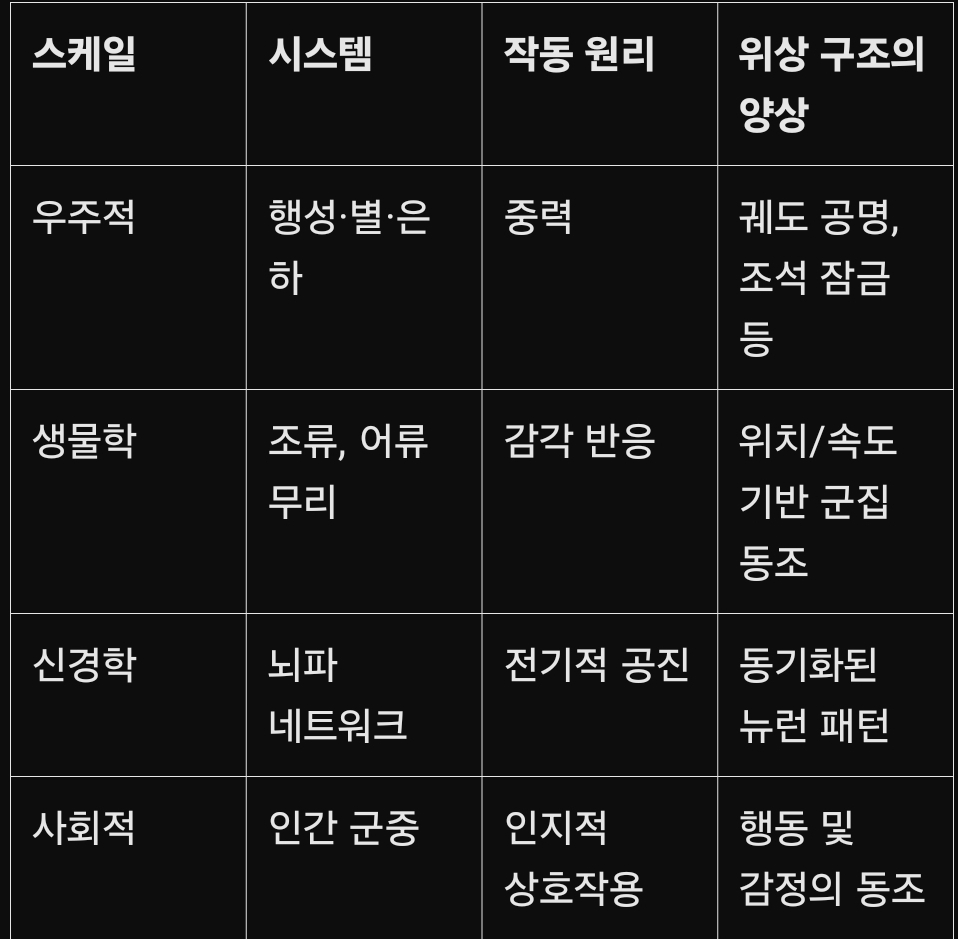
이러한 구조는 모두 다음의 특징을 갖는다:
국소적 상호작용 → 전역적 패턴 형성
중심 없는 자율조직
관계 기반 정의
---
5. 철학적 및 실천적 함의
존재론: 존재를 고정된 실체가 아닌, 동적인 관계 구조로 재정의함.
물리학: 상대성 이론 및 장 이론의 해석을 보다 직관적인 존재론적 기반 위에 놓음.
생물학: 자율적 군집행동, 생물계 네트워크 구조의 설명 틀 제공.
사회과학/심리학: 인간 존재 및 자아를 고정된 주체가 아닌 관계적 위상 구조로 해석 가능.
---
6. 결론
본 논문은 ‘존재는 위상 차이의 함수’라는 관점을 통해, 자연 현상에서 반복적으로 나타나는 프랙탈적 자기유사 구조를 설명할 수 있음을 제안한다. 이는 고전적 존재론을 넘어, 다층적·관계적 존재 구조에 대한 통합적 해석틀을 제공한다.
존재는 단일한 본질이 아니라, 상호적 위상 구조 속에서 패턴으로 드러나는 현상이며,
그 구조는 우주의 가장 작은 진동부터 가장 큰 은하까지 동일한 원리로 작동한다.
---
참고 문헌
1. 바버, 줄리언. (1999). 시간의 종말. 옥스퍼드 대학교 출판부.
2. 쿠진 외. (2005). 동물 집단 내 효과적인 의사결정과 리더십. 네이처.
3. 망델브로, B. (1982). 자연의 프랙탈 기하학. W.H. 프리먼.
4. 로벨리, 카를로. (2018). 시간의 질서. 리버헤드 북스.
5. 토노니, G. (2004). 의식의 정보통합이론. BMC Neuroscience.
---
---
The Ontology of Relational Phase: A Fractal Model of Emergent Existence through Relative Positioning
Author: I.M. Muante
Affiliation: Independent Institute of Theoretical Meta-Structures
Date: March 26, 2025
---
Abstract
This paper introduces the Ontology of Relational Phase, a philosophical framework proposing that all forms of existence are not defined by intrinsic properties or absolute coordinates, but emerge through dynamic, relative positioning within systems of interacting entities. By analyzing patterns found in cosmic celestial mechanics and collective animal behavior, particularly avian swarm dynamics, the paper posits that disparate phenomena across different scales demonstrate self-similar phase-dependent patterns. This suggests a fractal architecture to existence itself. The theory articulates existence as emergent from phase relationships, formalized through a mathematical abstraction, and applicable across physical, biological, and cognitive systems.
---
1. Introduction
The question "What is existence?" has long been pursued through ontological, cosmological, and biological perspectives. Classical ontology tends to emphasize inherent substance or fixed identity. However, emerging observations from complex systems and relational physics challenge this view. From gravitational interactions among galaxies to the collective behavior of animals, it becomes apparent that existence is better understood as relational and dynamic rather than absolute and static.
This paper introduces a theory termed Relational Phase Ontology, which postulates that existence is a function of relative phase interactions between entities, and that such patterns exhibit fractal self-similarity across scales.
---
2. Theoretical Background
2.1. Relative Motion in Celestial Systems
Modern astrophysics recognizes that no object in the universe possesses an absolute position. Movements of planetary bodies are only meaningful relative to other masses via gravitational fields. The Earth’s motion, for instance, is not meaningful in isolation but as a product of its gravitational phase with the Sun, Moon, and other celestial bodies.
2.2. Collective Animal Behavior
Swarming behavior in birds, particularly corvids (e.g., crows), presents complex emergent formations. These formations are not dictated by a leader or centralized controller but are generated by local phase relationships—each bird responding to its nearest neighbors. The result is a dynamic yet coherent pattern of movement. This local response structure closely parallels celestial phase dynamics at a different scale.
---
3. Central Hypothesis: Phase-Defined Existence
The central claim is as follows:
> Existence is not a solitary state, but a product of a system of relative phase differentials.
Let represent an entity. Its identity is defined not in isolation but as a function of phase difference with surrounding entities :
E = f(\Delta \phi_{1}, \Delta \phi_{2}, ..., \Delta \phi_{n})

Here, denotes the phase differential—temporal, spatial, or informational—between the entity and each reference.
---
4. Fractal Self-Similarity Across Scales
Despite scale or mechanism, systems of interaction—be they gravitational or perceptual—often give rise to self-similar patterns. This phenomenon aligns with the concept of fractal geometry, where similar structures recur at different magnitudes and in different domains.
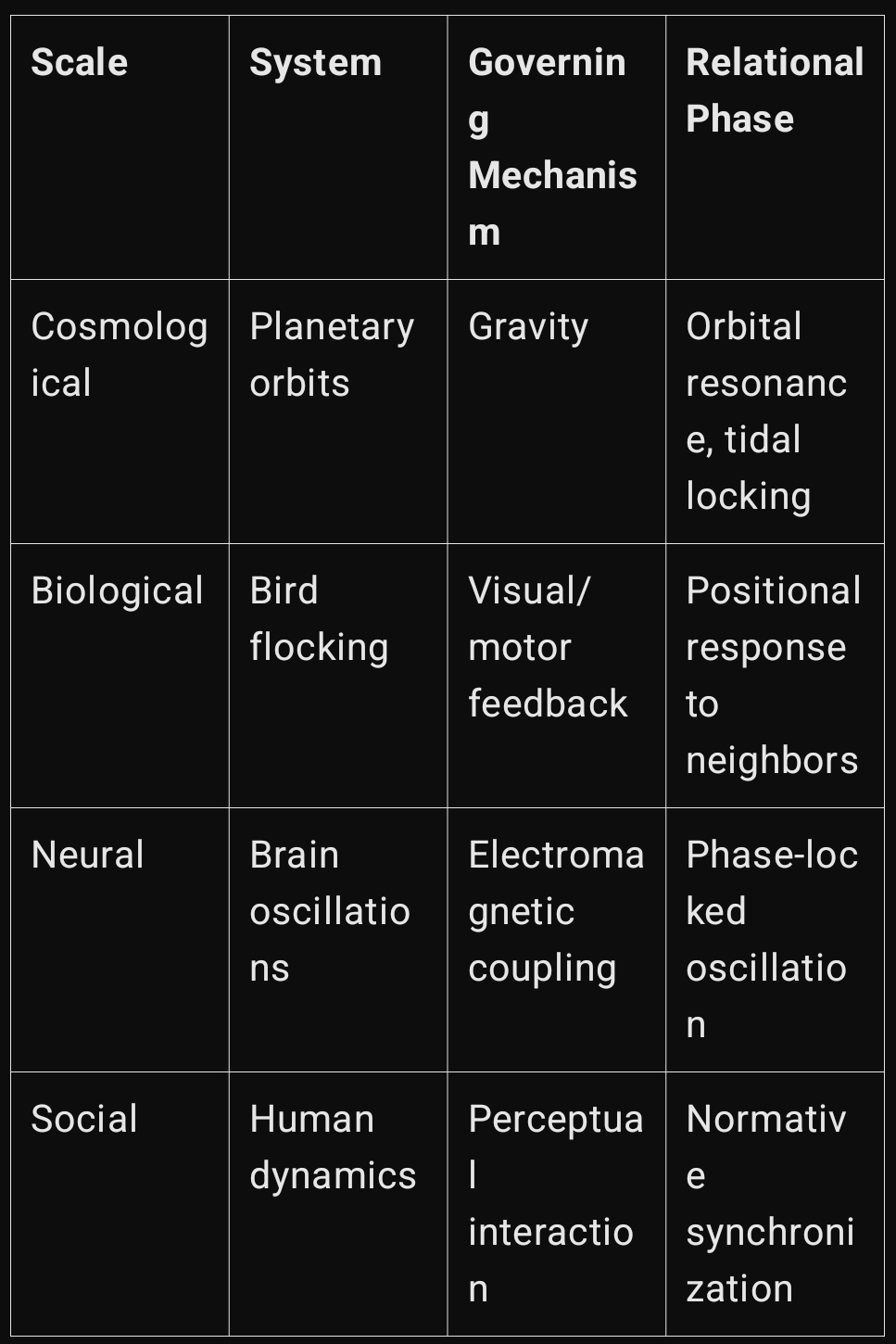
These examples suggest a universal template: entities do not operate in isolation, but emerge through synchronization and divergence of phases with others in their field.
---
5. Implications and Applications
Ontological Shift: Redefines existence as emergent, relational, and transient, rather than fixed and self-contained.
Physics: Offers a philosophical model compatible with relativistic frameworks and field theories.
Biology and Ecology: Provides a generalizable model for understanding coordination without central control.
Cognitive Science: Proposes a model for consciousness as emergent from phase interactions between neural systems and external stimuli.
---
6. Conclusion
The Ontology of Relational Phase suggests that the essence of existence lies not in absolute properties but in the pattern and rhythm of interactions. From the cosmos to cognition, systems exhibit fractal structures of relational phase dynamics. This philosophical approach seeks to provide a cross-disciplinary lens that unifies disparate phenomena through a common structural principle: existence as phase-dependent emergence.
---
References
1. Barbour, J. (1999). The End of Time: The Next Revolution in Physics. Oxford University Press.
2. Couzin, I.D., et al. (2005). Effective leadership and decision-making in animal groups. Nature.
3. Mandelbrot, B. (1982). The Fractal Geometry of Nature. W.H. Freeman.
4. Rovelli, C. (2018). The Order of Time. Riverhead Books.
5. Tononi, G. (2004). An information integration theory of consciousness. BMC Neuroscience.
---
'인공지능(ChatGPT) > 과학' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 양자 지평선: 양자컴퓨터 기술 현황 분석 및 투자 전략 보고서 (11) | 2025.08.11 |
|---|---|
| 후쿠시마 원전 사고 이후 현황 보고서 (3) | 2025.06.26 |
| 기억하지 않아도 괜찮은 이유: 유추와 창조의 힘 (0) | 2024.12.16 |
| 랑비에르 결절(Node of Ranvier) (0) | 2024.11.27 |
| 물질이란 에너지라는 주장에 대해서. (1) | 2023.01.22 |